The cart is empty!
Ask the Expert – What do Industry 4.0 and Industrial IOT Mean for Predictive Corrosion Management?
Dr Prafull Sharma, Chief Technology Officer, Corrosion RADAR
Dr Prafull Sharma, our ICorr Midlands Chair, currently serves as Chief Technology Officer of UK-based CorrosionRADAR Ltd., which is bringing innovative corrosion monitoring technologies using the Industrial Internet of Things (IOT). CorrosionRADAR invented a predictive CUI monitoring system, which is gaining global traction, addressing a big issue for the industry.
Dr. Prafull Sharma brings vast industrial experience, especially in the digitalisation of corrosion management, on which there are several inventions to his credit. Dr. Prafull did his PhD at Cranfield University, UK. He is also credited with over fifteen international patents and innovations.
For decades, corrosion has been one of the most significant risks to asset integrity. Across the globe, maintenance teams inspect as high a percentage as they can with the available resources. But many assets remain unchecked, leaving the potential for nasty (and costly) consequences.
Therefore, it’s no surprise that businesses have become interested in entering the era of Industry 4.0 while harnessing the potential of Industrial Internet of Things (IoT) and advancing digitalisation to control the global corrosion problem. Indeed, leading organisations are now embedding IOT methods into their processes.
Could developments in new sensing methods, device connectivity, and enhanced predictive data insights pave the way for a smarter approach
to mitigating or optimising expensive corrosion and inspection management programs?
The Global Corrosion Challenge
The most recent AMPP (NACE) Impact Study of 2016 highlighted what the industry is up against. The annual global cost of corrosion across all sectors is 2.5 trillion US dollars (Impact Study) . Meanwhile, corrosion under insulation (CUI) is estimated to be responsible for 60% of pipeline failures (Swift, 2019).
As assets age and portfolios widen, relying on traditional manual inspection processes can feel overwhelming. With numerous surfaces to inspect for signs of corrosion, asset deterioration can develop undetected.
What’s more, many assets are hard to reach without addressing additional safety issues and installing extensive scaffolding. And that’s before you know whether there’s something to remediate.
Asset inspection remains crucial, though. The cost of downtime due to failure or the need to make significant repairs can be eye-watering.
The industry has been stuck in this scenario for too long. However, digitalisation and industrial advances in IOT may provide an answer.
What is Industry 4.0?
Industry 4.0 represents the fourth industrial revolution, characterised by the integration of digital technologies, automation, and data-driven decision-making in manufacturing and industrial processes. It leverages advancements such as the Industrial Internet of Things (IOT), artificial intelligence (AI), big data analytics, and cloud computing to create smarter, more connected systems. In the context of predictive corrosion management, Industry 4.0 enables continuous monitoring of assets, predictive analytics for early detection of corrosion risks, and automated responses to mitigate failures, ultimately enhancing efficiency, safety, and cost savings in industries such as oil, gas, petrochemical, chemical processing, and infrastructure maintenance. In the context of predictive corrosion management, Industry 4.0 enables continuous data collection from sensors, advanced analytics to predict corrosion trends, and automated maintenance strategies—helping industries proactively manage asset integrity, reduce downtime, and extend equipment lifespan.
What is the Industrial Internet of Things (IoT)?
The Industrial Internet of Things (IoT) is a key pillar of Industry 4.0. It refers to the network of connected sensors, devices, and systems that collect, transmit, and analyse industrial data continuously. IOT enables smarter decision-making by integrating operational technology (OT) with information technology (IT), allowing industries to optimise processes, enhance efficiency, and improve asset reliability. In the context of predictive corrosion management, IOT plays a crucial role in monitoring environmental and material conditions, predicting corrosion rates, and enabling proactive maintenance. By leveraging IOT, industries can shift from reactive to predictive strategies, minimising failures and optimising asset performance.
Key Components of IOT in Predictive Corrosion Management for the Energy Industry
In energy industries such as oil, gas, and petrochemicals, IoT-driven predictive corrosion management is essential for maintaining asset integrity, minimising downtime, and ensuring operational safety. Below are the key components of IoT, along with best practices tailored to the energy sector.
Types of Sensors Used in Industries
1. Smart Sensors
Smart sensors are the foundation of IoT-driven predictive corrosion management, enabling continuous monitoring of asset integrity. These sensors measure critical parameters that influence corrosion, providing actionable insights for early detection and mitigation.
Examples of Smart Sensors in Corrosion Management
• Cathodic Protection (CP) Sensors: Monitor CP system performance
by measuring current, voltage, and potential shifts in buried or submerged structures.
• Coating Integrity Sensors: Detect coating degradation, disbondment, or permeability issues that could accelerate corrosion.
• Corrosion Rate Sensors: Measure corrosion rates using electrochemical techniques such as linear polarisation resistance (LPR) or electrical resistance (ER).
• Corrosion Under Insulation Risk Monitors: Use of wire sensors to monitor and locate high-risk locations of CUI.
• Environmental Sensors: Measure predictive parameters, such as humidity, temperature, pH, chloride, and oxygen levels, to assess corrosion risk factors.
•Wall Thickness Monitors: These devices utilise ultrasonic or electromagnetic techniques to detect metal loss in pipelines, tanks, and other structural components.
The following are some examples of best practices when
deploying sensors:
•Deploy multi-sensor arrays at high-risk locations, such as weld joints, bends, and submerged structures.
•Integrate sensor data with predictive analytics to detect early warning signs and optimise maintenance schedules.
•Use wireless and low-power sensors for remote and hard-to-access assets.
By leveraging a combination of these smart sensors, industries can gain a comprehensive understanding of corrosion dynamics and transition from reactive maintenance to predictive asset management.
2. Edge Computing
Edge devices process data locally near the sensor, reducing latency and enabling continuous decision-making.
• Apply AI-based edge analytics to filter noise and detect meaningful corrosion trends.
• Implement decentralised processing to reduce reliance on cloud connectivity in offshore and remote sites.
• Utilise ruggedised edge computing devices that can withstand extreme environmental conditions.
3. Connectivity and Communication Protocols
Reliable data transmission is crucial for IOT performance, especially in harsh environments such as offshore platforms and refineries.
Common Communication Protocols
• 5G and Private LTE Networks: Enable high-speed, low-latency communication for continuous monitoring.
• Choose communication protocols based on environmental constraints (e.g., use satellite-based IoT for offshore rigs).
• Ensure cybersecurity protocols such as VPNs and encryption for secure data transmission.
• Implement redundant communication pathways to prevent data loss in case of network failures.
• Industrial Ethernet and Modbus TCP/IP: Used in SCADA systems for secure and stable data transmission.
• LoRaWAN and NB-IoT: Ideal for long-range, low-power transmission in remote pipeline monitoring.
4. Cloud Computing and Data Storages
Cloud platforms aggregate and analyse data from multiple assets, providing a holistic view of corrosion risks across operations.
• Ensure compliance with industry standards (e.g., ISO 27001, NIST) for data security and regulatory requirements.
• Implement AI and Machine Learning (ML) models in the cloud to refine predictive maintenance strategies.
• Use cloud-based asset management platforms to centralise corrosion monitoring across multiple facilities.
5. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
(AI/ML)
AI-driven analytics enhance predictive capabilities by identifying patterns of corrosion and forecasting potential failure risks.
• Deploy AI-driven root cause analysis to identify and mitigate corrosion sources before they lead to failures.
• Train ML models using historical and continuous corrosion data to improve prediction accuracy.
• Use AI-powered digital twins to simulate corrosion scenarios and optimise maintenance planning.
6. Cybersecurity and Data Protection
With increased connectivity, securing IOT infrastructure against cyber threats is critical.
•Implement end-to-end encryption for sensor-to-cloud data transmission.
•Regularly conduct vulnerability assessments and apply firmware updates to IOT devices.
• Use multi-factor authentication and access controls for critical systems.
By integrating these IOT components effectively, oil, gas and petrochemical companies can transition from reactive corrosion management to predictive strategies, reducing unplanned downtime, improving asset longevity, and ensuring operational safety.
IOT Presents New Opportunities for Corrosion Management
Wherever you look, IOT appears to be the future. Smart cities, smart health, and digitalised education are a few examples. It’s the future for industry too. And for some sectors, it’s rapidly becoming the present:
•Advanced CUI monitoring methods using IOT also reduce the environmental impact of many assets. Catching problems early reduces the risk of deadly substances such as Methane leaking into the local environment (Environmental Defence Fund) , so digitalisation supports ESG strategies as well.
•Data-informed decision-making improves, and the risk of unexpected damage from corrosion significantly falls.
•Industry 4.0 has evolved IOT quickly, allowing remote connections to gather data for decision-making. This technological advancement is transforming how industries operate, providing benefits that many have yet to experience.
•Remote monitoring also improves personnel safety. With less need for routine inspections, maintenance teams can rely on data-based decisions to access locations where the data suggests a corrosion risk. Therefore, time in the field is smarter and safer.
•So, IOT enables wireless connectivity with devices attached to industrial assets. Devices that can continuously collect data 24/7 without the need
for physical inspection. Using a central software platform to collate every piece of insight, assets can be remotely monitored from anywhere in
the world.
•The power of this development is extensive. Organisations can utilise the technology to reach all their assets, regardless of location.
•While it’s hard to deny that new technology is an investment, it’s balanced against the typically high physical inspection and repair costs when people are restricted to a manual process. Given the unpredictability of CUI, you’re far more likely to encounter more significant damage when you lack access to remote monitoring.
IOT-Based Predictive Corrosion Management
in Action
Several technologies have developed to support remote monitoring and control of asset corrosion. Some are in their infancy, while large organisations use others daily. Many relate to internal corrosion as
well as recent advancements in external corrosion, such as corrosion
under insulation.
Internal Corrosion – Non-Intrusive Corrosion Monitoring
Ultrasonic Wall Thickness: Ultrasonic Testing (UT) thickness monitors are a key IOT-enabled tool for non-intrusive corrosion monitoring. These sensors utilise high-frequency sound waves to measure the remaining wall thickness of pipelines, vessels, and structural components, detecting metal loss caused by internal corrosion. Traditional UT inspections require manual measurements, but IOT-based UT monitors provide continuousdata without the need for shutdowns or physical access. By integrating with wireless networks and cloud platforms, these systems allow remote monitoring, automated trend analysis, and predictive maintenance planning — reducing inspection costs and minimising the risk of unexpected failures.
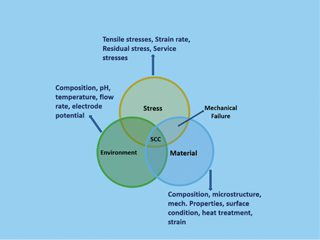
External Corrosion – Corrosion Under Insulation (CUI) Risk Monitoring
CUI is unpredictable and ‘hidden’, which is a huge concern for the oil, gas, and petrochemical industries.
• Damage doesn’t always develop near a damaged section of insulation. Instead, water from rain or humidity can ingress further, making it challenging to predict where corrosion might take hold.
• Many plants operate in locations that experience extreme heat or cold, making insulation necessary to maintain the temperature of liquids passing through pipes and tanks. Yet, insulation can trap moisture.
• Physical inspections require the removal of insulation and the installation of significant scaffolding to gain access, limiting what maintenance teams can see.
• The advance of IOT technology has now enabled oil, gas and petrochemical plants to install remote sensors that report early signs of asset deterioration due to CUI. Wirelessly connected, these smart sensors are embedded along the insulated structure and transmit data to an analytics dashboard. For example, they can monitor temperature gradients, humidity, and moisture ingress under insulation.
• With in-depth data insight from a wide range of assets—even those hard to reach—maintenance teams can make informed and prioritised decisions about where remedial work should be carried out. In this way, they mitigate problems before the damage spreads further and focus their physical activity on the areas at highest risk.
Cathodic Protection Remote Monitoring
Cathodic Protection (CP) remote monitoring is a crucial IOT application for managing external corrosion in buried pipelines, offshore structures, and storage tanks. CP systems utilise impressed current or sacrificial anodes to protect metal surfaces from corrosion; however, their effectiveness depends on maintaining proper voltage and current levels. IOT-enabled CP monitoring systems continuously track key parameters such as pipe-to-soil potential, current flow, and anode performance, transmitting continuous data to centralised platforms. This eliminates the need for manual site visits, ensures compliance with corrosion protection standards, and enables early detection of CP failures, thereby reducing the risk of costly asset degradation.
The Era of Predictive Monitoring
Remote corrosion monitoring, enabled by the advancement of IOT, presents a further benefit to managing asset integrity: prediction.
•Being able to monitor and predict where corrosion is likely to occur presents asset-intensive organisations with a significant opportunity to better control this primary operational risk. Thanks to IOT, embracing the capability of new industry technology will reduce maintenance costs and mitigate potential failures.
•By installing IOT remote monitoring systems with environmental sensors across your assets, you collect a huge amount of relevant and timely data. Using predictive analytics to spot patterns in the data, you can highlight risk areas before visible damage occurs.
•For example, CorrosionRADAR’s Clarity Dashboard provides data-driven insights into historical data, environmental factors, moisture, and corrosivity rate to predict corrosion progression. As data continues to populate the dashboard, the picture only becomes more apparent.
•Maintenance teams can then use risk maps and actionable insights to prioritise areas for physical inspection and repair. This optimises resource allocation and ensures the effectiveness of their corrosion management process.
Why Digital Twins Help in Corrosion Management?
As technology advances further, digital twins have become helpful in detecting and managing corrosion.
•By visualising your assets virtually, even when they’re out of easy reach, you can ensure optimum safety and maximise the service life of each piece of equipment. Digital twins can also help with compliance with safety and regulatory requirements, enhancing your reputation as a responsible operator.
•Digital twins are virtual replicas of physical assets, processes, or systems that mirror their real-world counterparts. Remote sensors, simulations, and machine learning can help create an interactive ‘twin’ that enhances monitoring and enables deeper analysis. It is worth noting that there are several definitions and connotations of Digital Twins in the industry, and the above is just one of them.
•Digital twins can enable detection at the earliest opportunity, making monitoring and maintenance more proactive. Analysing data from various sources, this holistic approach provides the most data-informed decision-making currently possible.
IOT is Shaping Future Corrosion Management
•IOT is rapidly paving the way for more effective corrosion control—a challenge that many industries have struggled to overcome for decades. Being able to remotely monitor your assets, wherever they are in the world, offers levels of insight many would welcome.
•More comprehensive data insight, available without physically inspecting assets, is transforming maintenance programmes for organisations worldwide. Not only does it help spot (and predict) corrosion earlier, but such insight also reduces maintenance costs and enhances safety.
•The moment you install remote IOT monitors to help control corrosion, your risk levels reduce as you collect widespread data. And this is only the beginning. As technology advances further, there’s no end to how it can help mitigate the incredibly costly risk of corrosion.
References
[1] NACE International, 2016. IMPACT breaks new ground in the study of corrosion management. Materials Performance, [online] Association for Materials Protection and Performance. Available at: https://impact.nace.org/documents/MP0316-Impact.pdf
[2] NACE International, 2014. Corrosion under insulation on industrial piping – a holistic approach to insulation system design. In: CORROSION 2014 Conference & Expo, 9–13 March, San Antonio, Texas. NACE International. Available at:
https://www.onepetro.org/conference-paper/NACE-2014-4084
[3] Environmental Defence Fund, n.d. Methane: A crucial opportunity in the climate fight. [online] EDF. Available at: https://www.edf.org/climate/methane-crucial-opportunity-climate-fight